 The website is in construction. New files will be uploaded as soon as they are available.
The website is in construction. New files will be uploaded as soon as they are available.
1922 - 1936
- 11-16 August 1924 - The International Congress of Mathematicians is held in Toronto under the chairmanship of John Charles Fields
-
444 mathematicians from 33 countries participate. The exclusion policy is confirmed. Salvatore Pincherle is elected chairman of the IMU. In section VI, History, Philosophy, Didactics, only two contributions by L.J. Crelier and by H. Fehr are dedicated to teaching. In particular Fehr deals with: L'Université et la préparation des professeurs de mathématiques (Proceedings of the International Mathematical Congress held in Toronto, August 11-16, 1924, edited by J.C. Fields, Toronto, 2 vols, The University of Toronto Press, 1928, II, p. 987).
 Toronto, University College, Meeting place of Sections I, II,VI
Toronto, University College, Meeting place of Sections I, II,VI - 22 June 1925 - Felix Klein dies (EM 24, 1924-1925, pp. 287-290)
- June 1926
- The International Research Council decides to invite Austria, Bulgaria, Germany and Hungary to become members of the Council and of the Unions attached to it. The German scientists refuse.
- 5 September 1928 - The International Commission on the Teaching of Mathematics is reconstituted on the occasion of the International Congress of Mathematicians, Bologna (3-10 September 1928) (EM, 27, 1928, pp. 326-327)
- The Congress is organised by the Italian Mathematical Union (created in 1922) whose President, Salvatore Pincherle, is also President of the International Mathematical Union. 826 mathematicians, from 36 countries, including Germany, take part in the work of the congress, without restrictions. The participation of the German mathematicians, non-members of the International Research Council, desired by Pincherle in the name of internationality of science, violates the rules of the International Mathematical Union. For this reason, during the General Assembly of the IMU, he submittes his "absolutely irrevocable" resignation from his position as President (Atti del Congresso Internazionale dei matematici, Bologna 3-10 Settembre 1928, 6 vols, Bologna, Zanichelli, 1929-1932, I, pp. 5-10, 83). Section VI , sees the presentation of ten papers specifically dedicated to the teaching of mathematics and also H. Fehr's account of the activities of the International Commission on the Teaching of Mathematics. N. Sakellariou from Athens presents the paper Projet pour la constitution d'une commission internationale pour l'enseignement des mathématiques (Atti del Congresso Internazionale dei matematici, Bologna 3-10 Settembre 1928, op. cit. III, pp. 157-158).
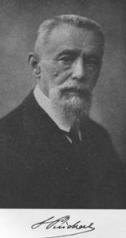 Salvatore Pincherle
Salvatore Pincherle
-
Section VI, under the chairmanship of G. Castelnuovo, submits for the approval of the Congress the proposal that the Commission be reconstituted in such a way that all the countries participating in the Congress are represented, and further proposes the extension of the mandate of the existing Central Committee, which will be enlarged with the co-optation of a new member (cf. Atti del Congresso, op. cit., I, p. 113).
The Central Committee thus consists of the following:
President D.E. Smith,
Vice-Presidents G. Castelnuovo (Rome), J. Hadamard (Paris),
Secretary General: H. Fehr,
Member W. Lietzmann (Göttingen).
Official languages: German, English, French, Italian.
Official organ: L'Enseignement Mathématique.
The study of questions concerning teacher training, proposed in 1914, is taken up anew. The related questionnaire is reviewed and expanded. - 1929-1933 - With the financial support of the American Delegation, the following papers from the various countries on the changes in the teaching of mathematics since 1910 are published:
-
France (A. Châtelet), Italy (F. Enriques), Switzerland (S. Gagnebin): EM 28, 1929, pp. 6-27, Germany (W. Lietzmann), England (L. Carson), Holland (J.E. Schrek): EM 28, 1929, pp. 258-286; Austria (K. Falk), United States (W.D. Reeve), Japan (A. Yayotaro): EM 29, 1930, pp. 113-156; Scandinavia (P. Heegaard), Czechoslovakia (Q. Vetter): EM 29, 1930, 307-325; Hungary (C. Goldziher): EM 30 1931, pp. 136-143; Russia (D. Sintsof): EM 32, 1933, pp. 81-87.
(see also The National Council of Teachers of Mathematics, Fourth Yearbook, New
York: Bureau of Publications, Teachers College, 1929).
1931 a reworked version of the questionnaire relating to the inquiry into theoretical and practical training of mathematics teachers in secondary schools proposed in 1914 is published (EM, 30, 1931, pp. 291-296) - 5-12 September 1932 - the International Congress of Mathematicians is held in Zurich under the presidency of Rudolf Fueter.
-
667 mathematicians from 35 countries participate. The solemn opening session is held in the amphitheatre of the école Polytechnique Fédérale.
 école Polytechnique Fédérale
école Polytechnique Fédérale
The inherent contradictions in the IMU lead to its being suspended. The General Assembly assignes to an international commission under the chairmanship of F. Severi (Rome) the task of studying the general question of permanent international collaboration in mathematics (Lehto 1998, p. 56-60). The Fields Medal which includes the motto "Transire suum pectus mundoque potiri"
The Fields Medal which includes the motto "Transire suum pectus mundoque potiri"
A woman mathematician, Emmy Noether (Göttingen), is invited to a give the plenary speech.
The late J.C. Fields's offer of awarding every four years, during the International Congresses of Mathematicians, two gold medals to two mathematicians "for outstanding achievements in mathematics" is accepted (Lehto 1998, p. 62). The first will be awarded in Oslo in 1936.
Section VIII, devoted exclusively to didactics and to the activities of the Commission, consists of 8 papers including those of H. Fehr and of D.E. Smith who present respectively a concise report on the activities of the Commission from 1928 to 1932 and its projects for the future (EM, 31, 1932, pp. 260-267)I therefore propose - writes Smith - that the present Commission proceed to reorganize itself and to make contact with the various countries, either through the national departments of education or through the leading national societies of teachers of mathematics and arrange to report in 1936 on the present general trend in the teaching of the subject. (Cfr. Verhandlungen des Internationalen Mathematiker-Kongresses Zürich 1932, Zürich, Orell Füssli Verlag, s.d., I Bericht und allgemeine Vortrâge, II Sektions-Vortrâge, II, p. 361)
G. Loria presents his general report on the subject La préparation théorique et pratique des professeurs de mathématiques de L' Enseignement secondaire dans les divers pays which will be published in full in EM, 32, 1933, pp. 5-20. The same issue will also include the reports from the national delegations, some of which have already appeared in journals of their home countries: Germany (W. Lietzmann, with appendix by G. Hamel), England (H. Neville), Austria (W. Wirtinger, H. Hahn, E. Kruppa), Belgium (A. Mineur, F. Sterkens) , Denmark (J. Mollerup), United States (E.R. Hedrick), France (G. Iliovici, J. Desforge), Hungary (E. Beke, A. Szücs, G.Toth), Italy (A. Perna), Norway (P. Heegaard), Poland (-), Switzerland (H. Fehr, E. Amberg), Czechoslovakia (Q. Vetter), Yugoslavia (J. Karamata). (EM, 32, 1933, pp. 169-254 and 360-400 ) Cf. also Publications du Comité central rédigées par H. Fehr, La préparation théorique et pratique des professeurs de mathématiques de L'Enseignement secondaire dans les divers pays, Genève 1934). Gino Loria
Gino Loria - 12 September 1932 - During the Congress the International Commission on the Teaching of Mathematics is invited to continue its activities for a further four years
-
The Central Committee will be composed as follows:
President J. Hadamard,
Vice-Presidents P. Heegaard (Oslo) W. Lietzmann (Göttingen), G. Scorza (Naples), Secretary General and Treasurer Fehr (Geneva). H. Neville (Reading) will be co-opted.
Official languages: German, English, French, Italian.
Official organ: L' Enseignement Mathématique.
A new subject for study is proposed: Present trends in the teaching of mathematics in the various countries (EM. 31, 1932, p. 266). - 1935
-
The Central Committee decides not to impose a questionnaire, but rather recommends the following guidelines for drawing up the report on the matter Present trends in the teaching of mathematics in the various countries (EM. 34, 1935, pp. 112-113) :
I. School organisation - New types of schools;
II. Modern trends concerning the purpose of the teaching of mathematics - Study programmes;
III. Exams - Exam programmes for university entrance (Bachelor's degree, highschool diploma, etc.);
IV. Teaching methods - the links between the different branches of mathematics - The place of applied mathematics- Textbooks;
V. Training of mathematics teachers;
VI. Miscellaneous. - 15 September 1935, with the promulgation of the Nuremberg Laws, A. Hitler's national socialist regime institutionalises its discrimination against Jews. Hundreds of Jewish university lecturers are removed from their teaching posts and some of the most important German scientists are forced to leave Germany
- 13-18 July 1936 - the International Congress of Mathematicians is held in Oslo under the presidency of Carl Størmer
-
487 mathematicians from 36 countries participate.
After the Congress of Zurich, the international commission under the chairmanship of F. Severi (Rome), charged to study the question of permanent international collaboration in mathematics, had set up a smaller Executive Committee (F. Severi, W. Blaschke, C. Carathéodory, G. Julia and H Weyl). After four meetings the Executive Committee announces its failure:La Commission nommée par le Congrès de Zurich a vivement regretté l'absence de son président Severi. Elle n'a pu, pour diverses raisons, arriver à un accord unanime sur la question d'une organisation internationale des mathématiciens. Elle souhaite que dans l'avenir la question posée puisse recevoir une solution. (Cf. Comptes rendus du Congrès International des Mathématiciens, Oslo 1936, Oslo, A. W. Brøggers Boktrykkeri, 1937, I, p. 47)
Section VIII, devoted exclusively to didactics and to the work of the Commission, contains two contributions on the teaching of specific subjects: the first on a "method for demonstrating the qualitative properties of differential equations by means of cinematograph films" and the second on the extraction of the roots of a number.
On reporting on the work of the Commission, H. Fehr observes:Au moment où, dans d'autres domaines, la coopération internationale rencontre encore des obstacles, nous sommes heureux de pouvoir faire constater ici que les travaux de la Commission ont pu se poursuivre dans un excellent esprit de compréhension et de collaboration. (Cf. Comptes rendus du Congrès International des Mathématiciens, Oslo 1936, op. cit. I, p. 47)
The reports from the various countries on the theme of Present trends in the teaching of mathematics in the various countries follow and will be presented in full in L'Enseignement Mathématique: Germany (W. Lietzmann), England (H. Neville), Austria (E. Dintzl), Denmark (J. Mollerup), France (J. Desforge, G. Iliovici), Greece (P. Zervos), Hungary (T. Jelitai): EM 36, 1937, pp. 236-262 ; Japan (M. Kuniyeda), Norway (K. Piene), Poland (S. Straszewicz), Romania (G. Tzitzéica), Switzerland (H. Fehr): EM 36, 1937, pp. 357-388 ; Sweden (A. Wahlgren): EM 37, 1938, pp. 205-211 . - 15 July 1936
-
the Commission decides to confer the title of Honorary Member,
in recognition of their efforts, on: E. Beke (Budapest), Ch. Bioche (Paris), G. Castelnuovo (Rome), S. Dickstein (Warsaw), F. Enriques (Rome), Farid Boulad Bey (Cairo), G. Loria (Genoa), M. Petrovitch (Belgrade) and W. Wirtinger (Vienna). (Cf. Comptes rendus du Congrès International des Mathématiciens, Oslo 1936, op. cit. II, p. 289)
 Guido Castelnuovo
Guido Castelnuovo Samuel Dickstein
Samuel Dickstein Federigo Enriques
Federigo Enriques Farid Boulad Bey
Farid Boulad Bey Wilhelm Wirtinger
Wilhelm Wirtinger Gino Loria
Gino Loria Mihailo Petrovitch
Mihailo Petrovitch Emanuel Beke
Emanuel Beke
- 18 July 1936 - the Commission and the Central Committee in office are invited to continue their activities (EM 35, 1936, pp. 388).

Felix Klein
Table of the publications of the various countries of the International Commission on the Teaching of Mathematics
| Pamphlets or volumes | Number of papers | Pages | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Central Committee | 11 | 19 | 561 |
| Germany | 53 | 53 | 5571 |
| Argentine Rep. | 1 | 1 | 24 |
| Australia | 1 | 6 | 79 |
| Austria | 13 | 12 | 776 |
| Belgium | 2 | 5 | 366 |
| Denmark | 1 | 10 | 107 |
| Spain | 3 | 10 | 165 |
| United States | 18 | 18 | 1499 |
| France | 5 | 45 | 674 |
| Holland | 1 | 13 | 151 |
| Hungary | 9 | 9 | 294 |
| British Isles | 32 | 39 | 921 |
| Italy | 10 | 11 | 268 |
| Japan | 2 | 16 | 788 |
| Romania | 1 | 1 | 16 |
| Russia | 7 | 11 | 295 |
| Sweden | 8 | 8 | 229 |
| Switzerland | 9 | 13 | 781 |
| 187 | 300 | 13565 |
